From coffee machines to paint shops: IIoT at the cutting edge
February 13, 2019 | By: Marc DeCarlo | Category: IOT & 5G
The Freshwater Trust (TFT), together with IBM Research and SweetSense, a provider of low-cost satellite connected sensors, are partnering to pilot technologies which can accurately monitor and track groundwater use in one of the largest and most at risk aquifers in North America.
As part of Enterprise IoT Insights‘ investigation into edge-cloud setups in industrial plants, we have unearthed a number of informative case studies, showing how manufacturing companies and technology providers are collaborating to bring intelligence closer to the action.
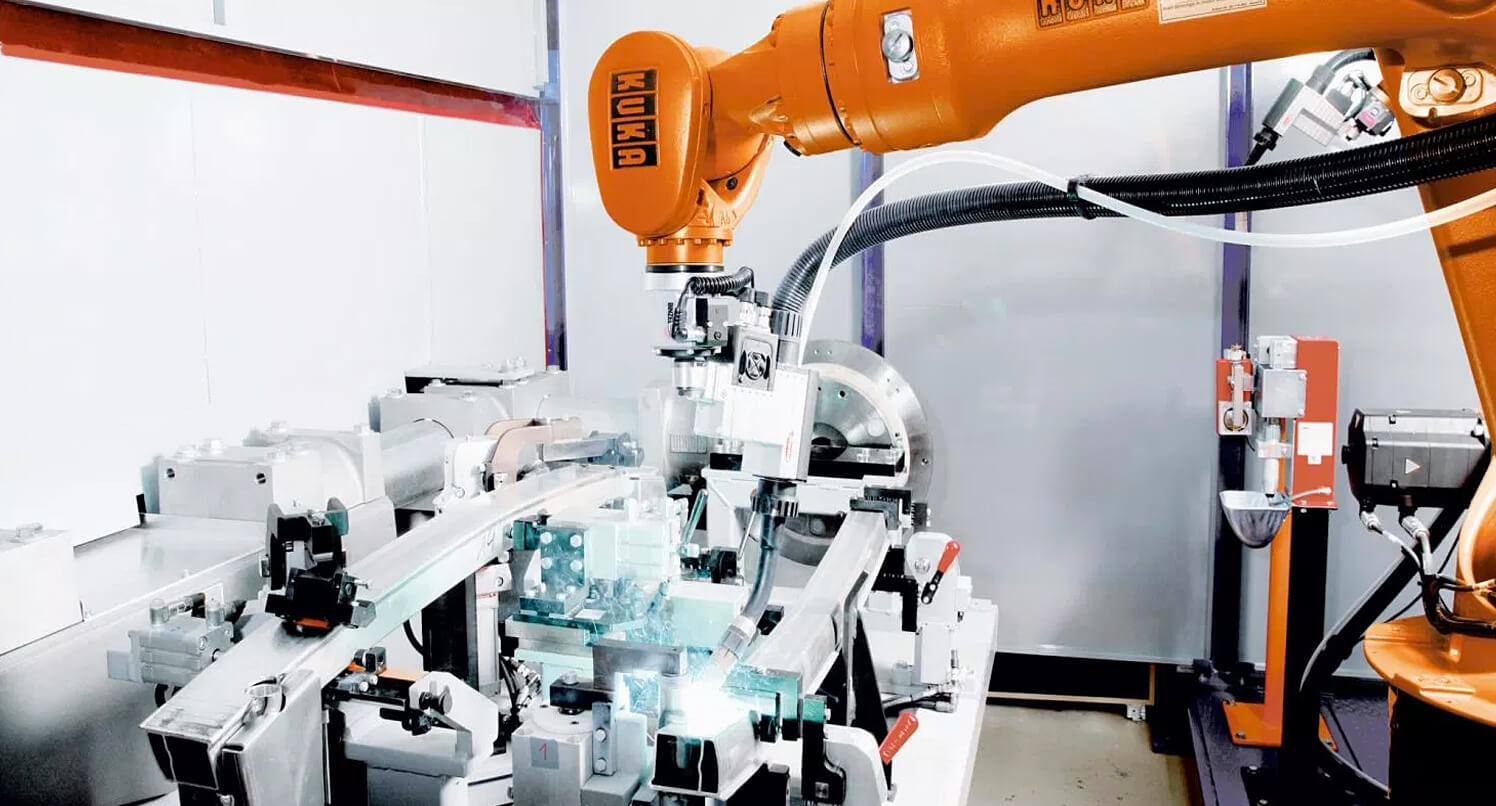
Kuka Robots | Factory robots
In one factory, Kuka Robots employs between four and eight robots per station, at 180 stations, to do stud welding. They weld about two studs per second, but they were recording a failure rate of four-to-eight per cent.
Software AG developed a machine learning model – trained in the cloud with historical data about stud positions, as well as welding parameters around materials and temperatures, and deployed that at the edge – to run on industrial PCs attached to the robots.
The plant is able to make proactive corrections at the first hint of predicted errors, and has lowered that error rate to an almost negligible level.
Certuss | Steam generators
German company Certuss produces low-noise steam generators for continuous operation. The devices are used in various fields of application, including to sterilise surgical instruments.
As they are often involved in multi-stage production, there is a potential for errors that cannot be ignored – even minor faults can have a negative impact on the production result. To counteract this, Certuss has set up a real-time analytics and predictive maintenance service using Software AG’s Cumulocity IoT platform.
The solution makes it possible to analyse about 60 parameters – pressure, temperature, water level, for example – for each steam generator in real time. With the data obtained, predictions can be made as to when and at which point in the production chain faults will occur. In addition, the required amount of steam can be determined via remote configuration, which in turn can reduce energy costs.
Lyreco | Office supples
Lyreco is a major supplier of office and workplace solutions, including high-quality coffee machines and matching coffee capsules. To keep a constant eye on the stock of capsules and the functionality of the machines for corporate customers, the company implements an IoT solution that analyses both the quantity of capsules available and the relevant functional parameters of the coffee machines in real time.
The machine data is integrated into Lyreco’s SAP ERP system and inventory management is fully automated, resulting in cost savings. This makes it possible to supply corporate customers on time or send a technician in the event of a technical failure. By using the IoT solution, the company was able to significantly reduce situations where customers were running out of stock or coffee machines were out of order.
Anon | Paint shops
Individual users who require groundwater amounts beyond their share cap will be able to “purchase” groundwater shares from users who do not require all of their supply at a market-regulated rate, IBM said.
Software AG has kitted out an unidentified manufacturer of automotive painting robots with its Apama streaming analytics and Zementis predictive analytics solutions in order to engage machine learning at the edge and detect defects in paint jobs in real time.
Prior to Software AG’s involvement, the manufacturing company had taken five key measures from sensor readings every eight milliseconds to gauge the quality of the paint jobs. But it was still experiencing an unacceptable number of quality issues.
With Software AG, in a hybrid edge-cloud setup, it trained some of that data in the cloud and deployed a machine learning model on an industrial PC connected to the painting robot at the edge.
It discovered only four of the measures were producing helpful data, detected that a malfunctioning optical sensor, damaged by paint particles, was undermining the IoT deployment, and increased the quality if its work as a consequence.
Enterprise IoT Insights is hosting an editorial webinar, entitled AI and IoT at the cutting edge – when to move intelligence out of the cloud and closer to the action, on February 14.

